What is Graphql Zeus ?
Graphql-Zeus is a strongly typed GraphQL request builder. It basically generates Typescript types for your GraphQL endpoint so that you can directly write TS code that is type-safe instead of writing graphql queries. Considering the fact that GraphQL was written at Facebook for this very reason it makes sense to use GraphQL this way.
Its makes writing production code a breeze with type safety. You can use things like Hasura and Github endpoints without worrying about return types. You can checkout the project below:
github.com/graphql-editor/graphql-zeus, Docs
When you use Postgres to persist data one of the many advantages it offers is that it offers both a relational SQL store and a JSON field support which is extensible. JSONB is a type of JSON field that uses Binary trees for fast processing. This allows us to perform effecient search operations over them. Ready to use servers such as Hasura declare these fields as scalars in GraphQL and return the inside value.
When using GraphQL Zeus this soon starts to become an issue as all values supplied in graphQL zeus typescript is expected to be in typescript types. The expected value in the predefined schema for a JSONB field exists as:
# zeus.ts
jsonBField: ValueTypes["jsonb"] | undefined | null | Variable<any, string>
# The ValueTypes["jsonb"] maps to
["jsonb"]:unknown;
This means that at the time of making request the TS runtime has no idea about what type to expect.
await hasura('mutation')({
insert_object: [
{
object: {
jsonBField: {
hello: "world"
}
}
},
{
jsonBField: true
}
]
})
# Returns error: Invalid GraphQL request
The above GraphQL shows no error in Typescript but the GraphQL request fails.
Solution
Solution 1: A workaround
A very simple fix is to just use the JSON.stringify()
...
{
object: {
jsonBField: JSON.Stringify({
hello: "world"
})
}
},
...
That works but the JSONB store now just holds the given value as string. Which means that you cannot perform other useful queries over it.
Solution 2: Using Variables
Since graphql-zeus v5.0 you can use variables to supply JSONB fields with values during insert. This requires a special function $. 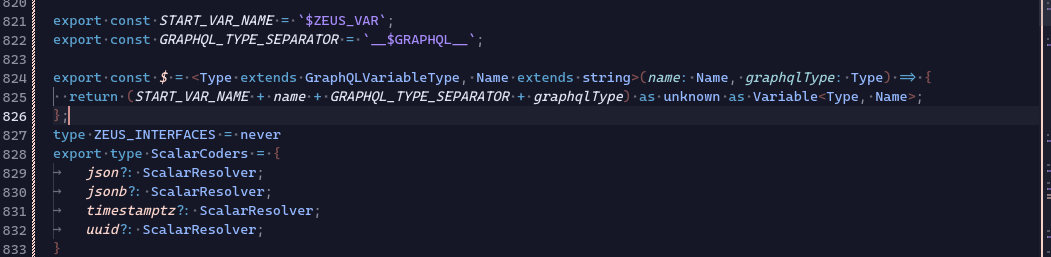
The function takes two arguments:
- Variable name
- Variable type
Here's the code to make the above insert work:
await hasura('mutation')({
insert_object: [
{
object: {
jsonBField: $(`jsonVar`, 'json')
}
},
{
jsonBField: true
}
]
}, {
variables: {
jsonVar: {
hello: "world"
}
}
})
I hope this helps!